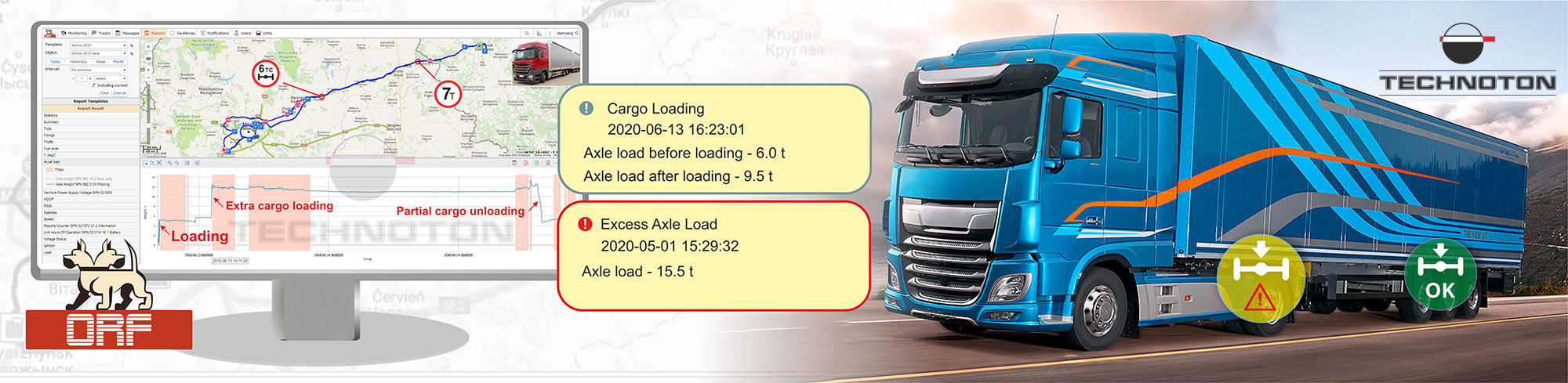
Axle load monitoring
Axle load monitoring is useful for vehicle fleets for several reasons. Firstly, exceeding axle load may result in fine for overloading when vehicle stops at weighing station. Secondly, loading vehicle in excess of axle load limit defined by data sheet shortens vehicle’s life cycle – early breakdown and extra costs for repairing suspension system and vehicle body, higher load on engine and increased fuel consumption.
From the other hand, under-loaded vehicle means reduced profitability of transportation and lower profit margins of vehicle owner: a vehicle uses fuel for “self-transportation”, wear out still occurs, driver gets salary irrespective to the amount of cargo in vehicle or semi-trailer.
One of the methods to optimize vehicle load – manual calculation of load per axle. However, the method is labor-intensive, takes much time, and obtained results should be transferred to vehicle telematics system manually as well.
Automated axle load control system is more convenient, accurate and quick way of truck and trailer weighing.
No time for reading?
Benefits from axle load monitoring system
- Avoiding losses caused by fines for exceeding axle load;
- Live axle load measurement by driver during cargo loading;
- 24/7 online axle load monitoring of all vehicles in fleet;
- Instant notifications on exceeding axle load limit;
- Registration of places, where vehicle is loaded and unloaded;
- Onboard weighing of truck and cargo;
- Optimization of cargo load, increasing profitability of fleet;
- Reducing truck maintenance costs and excluding extra costs for early repair;
- Excluding vehicle misuse – transportation of unregistered and unauthorized cargo;
- Remote diagnostics of vehicles with air suspension system.
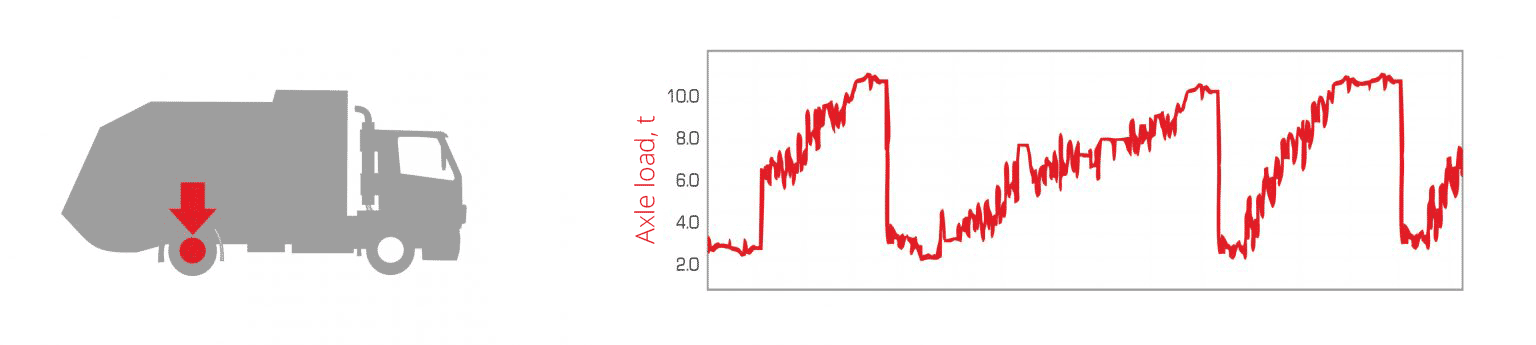
Axle measurement can be implemented as a stand-alone truck axle load monitoring system or as an integrated part of GPS vehicle tracking, i.e. telematics system with axle weight measurement feature. Axle load measuring can be performed on various vehicle types – road trucks and trailer/semi-trailers, dump trucks, garbage collection vehicles, buses, public utility vehicles.
Methods of axle weight measurement
A) Axle load sensor installation
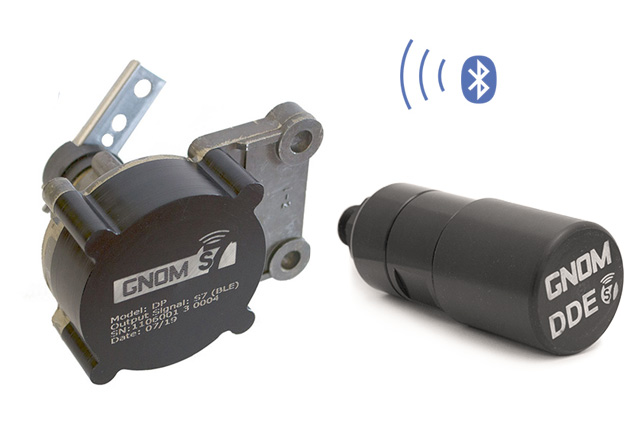

Quite often, additional sensors are used for axle load monitoring systems. For example – GNOM axle load sensors. The sensors can transmit measured axle load parameters over the wire or over the air (BLE, Bluetooth 4.X).
To obtain high accuracy of data, it is necessary to carry out axle load sensor calibration after it is installed: measured loads are placed one by one inside vehicle’s body and/or trailer and correspondence table between axle weight and sensor’s output signal is compiled.
Axle load sensor sends data to a telematics unit (e.g. GPS tracker), and then data is sent to online fleet management software. When using wireless GNOM axle loads sensor with BLE, driver can carry out onboard weighing during cargo loading and thus prevent exceeding axle load limit. GNOM will send data to a telematics unit and to driver’s smartphone simultaneously – axle load data will be available in smartphone app.
![]() Advantages:
Advantages:
- Possibility to be installed on vehicle with leaf spring suspension system;
- Data accuracy is usually higher comparing to CAN bus data;
- Can be used for diagnostics of air suspension system during technical check up;
- Allows axle load data monitoring via BLE on smartphone (wireless GNOM sensors).
![]() Disadvantages of additional sensors:
Disadvantages of additional sensors:
- Requires qualified technician for proper sensor installation;
- Calibration of sensor and telematics unit configuration are required.
B) Reading axle weight from CAN bus
Majority of modern vehicles are equipped with CAN j1939 data bus. T-CAN may contain axle load data obtained from standard vehicle sensors. Still, data presence can not be determined in advance and should be confirmed by installation technician. The technician goes to vehicle, connects to CAN bus and reads the data trying to find necessary CAN parameters.
Sometimes, axle load measurement using CAN J1939 data is not possible because the data is corrupt or encrypted.

![]() Disadvantages:
Disadvantages:
- Axle weight data is rarely available in CAN bus;
- No data in CAN bus of vehicles with spring suspension;
- Not possible to use on old vehicles, which don’t have CAN bus;
- Accuracy of CAN data is often lower comparing to additional sensors;
- No CAN bus data when ignition is off.
![]() Advantages:
Advantages:
- Low cost of solution itself (but the preparation works could be more expensive);
- Easy to install contactless CAN bus readers can be used for getting axle weight data;
- CAN bus readers are quicker to install then additional axle load sensors.

