Fuel consumption monitoring
Fuel consumption monitoring for vehicles and stationary objects allows a machinery-owner or fleet operator to solve a number of tasks:
- Optimizing machinery operation modes
- Engine hours and machinery downtime monitoring
- Recalculation of fuel consumption quotas
- Fuel theft prevention
- Prediction of maintenance date
To achieve optimal operating mode of vehicles:
- a driver can select resource-saving operation mode of engine by using RPM and fuel rate data;
- a mechanic can monitor fuel consumption information using online telematics system, remotely supervise technical condition of engine and fuel system, schedule technical maintenance taking into account real operating conditions of the equipment.
Almost any fleet owner faces fuel theft during vehicle or stationary machinery operation. The highest percentage of fuel misuse occurs with construction, agricultural and other machines, where fuel is accounted according to engine hours. Fuel tank draining, underfilling fuel in a tank, fraud with cash vouchers and fuel cards are the most common methods of fuel theft. They can be eliminated by introducing fuel consumption monitoring system.
No time for reading?
Benefits of implementing fuel consumption monitoring
Control of fuel consumption allows eliminating fuel theft in a fleet and thereby helps to reduce total fuel expenses and fleet costs.
Another important task is solved – engine operating time monitoring. That helps fleet manager to exclude inappropriate use or excessive downtime of the machinery.
Engine operation time recording also helps to shift to a performance-based pay system for drivers and operators of the equipment. That means drivers are paid for actual working time and achieved fuel economy score.
Fuel consumption monitoring system allows machinery-owner to recalculate fuel consumption quotas for each unit of equipment.
Our experience shows that fleets, which operate less common tractors or special vehicles, have just a general idea of the real consumption of diesel fuel. The consumption rates (quotas) approved by governmental bodies or by the company’s internal documentation is also inaccurate because they do not include influence of machinery working conditions.
Thus, the implementation of a fuel consumption control system gives fleet-owner a multi-directional economic effect:
- Increase of fleet performance
- Higher fuel economy and savings on fuel and lubricants
- Introduction of performance-based pay system for work actually performed
- Extended machinery lifetime, a decrease of repair and maintenance costs
Ways of fuel consumption monitoring
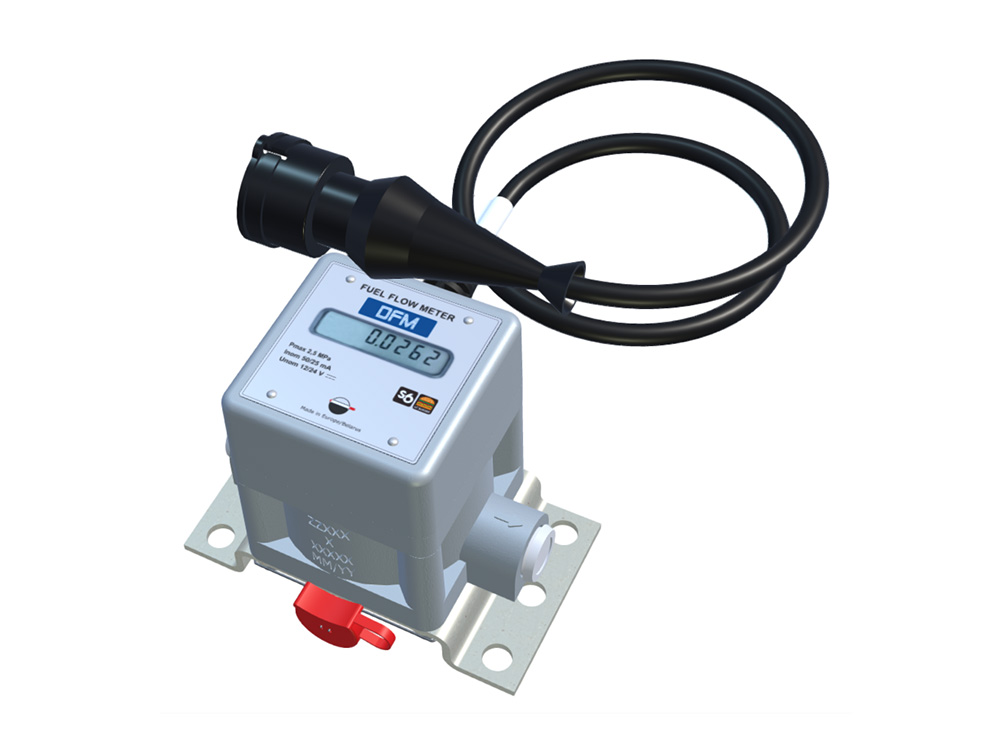
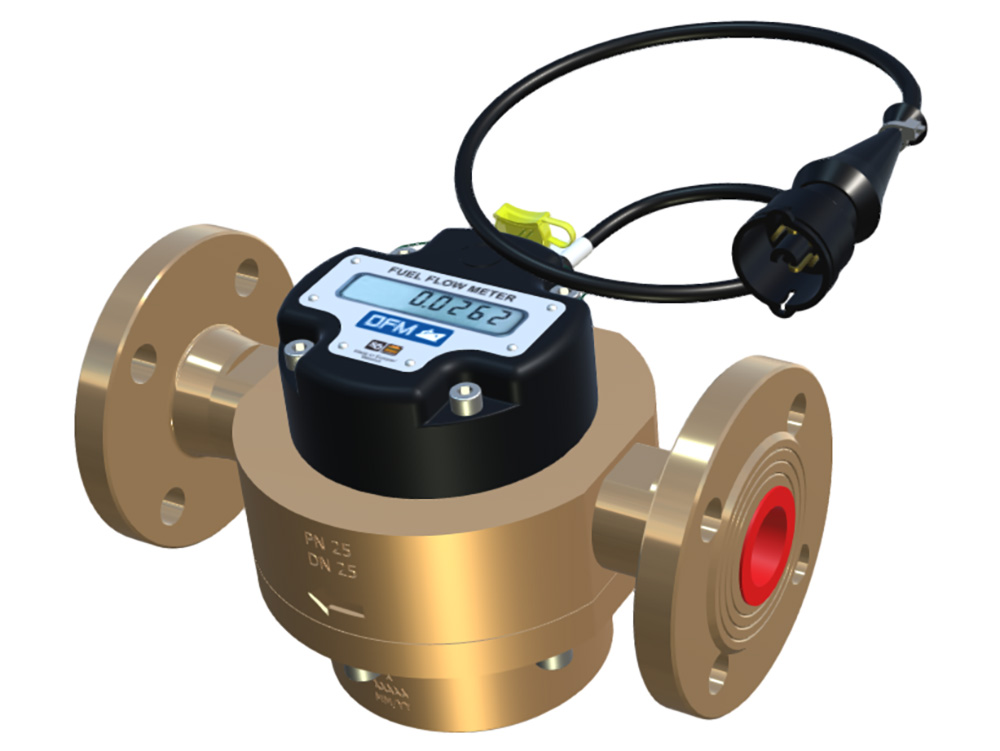
1. Fuel consumption monitoring by measuring fuel flow rate in engine’s fuel lines
This method differs from all others in that measurement of real fuel consumption is carried out, because flowmeter is installed in the fuel line of engine.


![]() Disadvantages:
Disadvantages:
- Fuel flow sensor installation requires time and sufficient qualification of installation specialist
- Installation costs are higher than for other fuel consumption control methods
![]() Advantages of fuel flow meter:
Advantages of fuel flow meter:
- High accuracy of fuel rate measurement
- Fuel consumption is correctly measured even for short operation periods
- Applicable for off-road (also railroad and water) vehicles, rough terrain has no influence on measurement accuracy
- Helps to follow fuel system’s and engine’s health, allows implementing predictive technical maintenance
2. Fuel consumption monitoring by detecting fuel level and volume change in a fuel tank
This method uses data from additional fuel level sensor, which measures current fuel level in a tank, and detects fuel tank filling-ups and fuel draining volumes.


![]() Disadvantages of fuel consumption control using level sensor:
Disadvantages of fuel consumption control using level sensor:
- Relatively low accuracy, especially in flat-shape fuel tanks
- Impossibility to measure fuel consumption during short operation periods, when fuel volume is not changing distinctly
- Hard to measure slow fuel draining from tank and impossible to detect fuel theft from return fuel line
- Not applicable for machinery operated in rough terrain, quarries, mines where fuel in tank fluctuates noticeably
![]() Advantages of fuel consumption measurement using fuel tank data:
Advantages of fuel consumption measurement using fuel tank data:
- Relatively low price
- No intervention into engine fuel supply system
- Fuel tank refilling and fuel draining volumes can be measured
3. Fuel consumption data from CAN J1939 bus
This method uses ECU data, which is available in CAN J1939 bus or J1708. CAN bus data is based on calculation algorithms applied by engine manufacturer and uses a predefined constant of fuel injection volume and measured duration of opening nozzles.
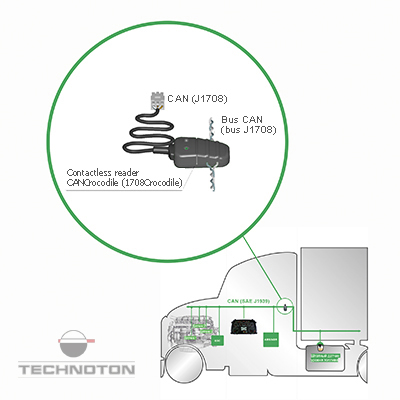

![]() Disadvantages of using CANbus data for fuel consumption measurement:
Disadvantages of using CANbus data for fuel consumption measurement:
- Low accuracy – indirect fuel control method (uses calculation method)
- Data can be “hidden” by engine manufacturer, i.e. inaccessible for reading
- Data can be erratic, corrupted or missing – typical for older vehicles
![]() Advantages of fuel consumption control using CAN J1939 data:
Advantages of fuel consumption control using CAN J1939 data:
- Low cost of data reading equipment
- Ease connection to CANbus and J1708 bus




